Asylo API Overview
Asylo provides strong encapsulation around data and logic for developing and using an enclave. In the Asylo C++ API, an enclave application has trusted and untrusted components. The API has a central manager object for all hosted enclave applications.
The following are the main classes for developing and using an enclave.
-
TrustedApplicationis the trusted component of an enclave application that is responsible for sensitive computations. -
EnclaveClientis the untrusted component of an enclave application that is responsible for communicating messages with the trusted component. -
EnclaveManageris a singleton object in the untrusted system that is responsible for managing enclave lifetimes and shared resources between enclaves.
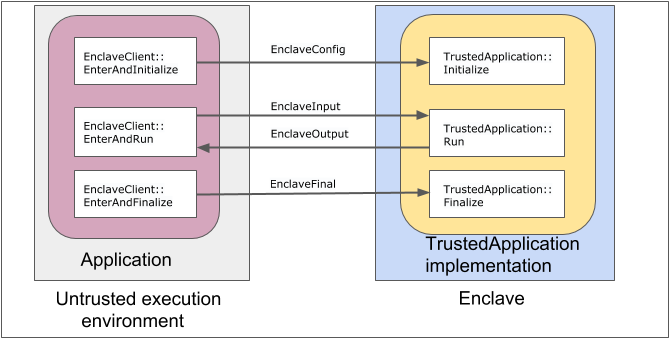
We refer to the process of switching from an untrusted execution environment to a trusted environment as entering an enclave. Every enclave provides a limited number of entry points where trusted execution may begin or resume.
Trusted environment
The trusted environment consists of one or more enclaves, which protect code and
data in a sensitive workload. To create an enclave, define a class which
inherits from TrustedApplication and implement the logic to host in the
enclave.
TrustedApplication class
The TrustedApplication class declares methods corresponding to each entry
point defined by the Asylo API.
Initializeinitializes the enclave with configuration values that are bound to the enclave’s identity. This should be used for security-sensitive configuration settings.Runtakes input messages from the untrusted environment code, performs trusted execution, and returns an output message to the untrusted environment.Finalizetakes finalization values from the untrusted environment and is called before the enclave is destroyed.
If any of these methods are not overridden, they simply return an OkStatus.
Untrusted environment
The untrusted API provides methods analogous to the enclave entry points that
are defined by a TrustedApplication. These methods implement the necessary
machinery to safely cross the enclave boundary. The inputs to these methods are
extensible by the developer.
EnclaveClient class
The EnclaveClient class is responsible for communicating messages with the
trusted component.
EnterAndInitializepasses enclave configuration settings and optional user-defined configuration extensions to the enclave. The configuration information is essential to the identity of the enclave.EnterAndRunpasses an input message to the enclave, and receives an output message from the enclave. This method may be called an arbitrary number of times with different inputs after the enclave has been initialized.EnterAndFinalizepasses enclave finalization data to the enclave.
Both EnterAndInitialize and EnterAndFinalize are private methods that are
called by the friend class EnclaveManager.
EnclaveManager class
The EnclaveManager class is responsible for creating and managing enclave
instances. This class is a friend class to EnclaveClient.
-
LoadEnclaveinitializes the enclave with a call toEnterAndInitialize. -
DestroyEnclavedestroys the enclave with a call toEnterAndFinalize.
Entering an enclave from an untrusted execution environment
Entering an enclave is analogous to making a system call. An enclave entry point implements a gateway to sensitive code with access to the enclave’s resources. Arguments are copied into the enclave on entry and results are copied out on exit. The following is a snippet from our Getting Started guide to writing your first Asylo application.
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
absl::ParseCommandLine(argc, argv);
constexpr char kEnclaveName[] = "demo_enclave";
const std::string message = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_message);
LOG_IF(QFATAL, message.empty()) << "Empty --message flag.";
const std::string enclave_path = absl::GetFlag(FLAGS_enclave_path);
LOG_IF(QFATAL, enclave_path.empty()) << "Empty --enclave_path flag.";
// Part 1: Initialization
// Prepare |EnclaveManager| with default |EnclaveManagerOptions|
asylo::EnclaveManager::Configure(asylo::EnclaveManagerOptions());
auto manager_result = asylo::EnclaveManager::Instance();
LOG_IF(QFATAL, !manager_result.ok()) << "Could not obtain EnclaveManager";
// Prepare |load_config| message.
asylo::EnclaveLoadConfig load_config;
load_config.set_name(kEnclaveName);
// Prepare |sgx_config| message.
auto sgx_config = load_config.MutableExtension(asylo::sgx_load_config);
sgx_config->set_debug(true);
auto file_enclave_config = sgx_config->mutable_file_enclave_config();
file_enclave_config->set_enclave_path(enclave_path);
// Load Enclave with prepared |EnclaveManager| and |load_config| message.
asylo::EnclaveManager *manager = manager_result.value();
auto status = manager->LoadEnclave(load_config);
LOG_IF(QFATAL, !status.ok()) << "LoadEnclave failed: " << status;
// Part 2: Secure execution
// Prepare |input| with |message| and create |output| to retrieve response
// from enclave.
asylo::EnclaveInput input;
asylo::EnclaveOutput output;
SetEnclaveUserMessage(&input, message);
// Get |EnclaveClient| for loaded enclave and execute |EnterAndRun|.
asylo::EnclaveClient *const client = manager->GetClient(kEnclaveName);
status = client->EnterAndRun(input, &output);
LOG_IF(QFATAL, !status.ok()) << "EnterAndRun failed with: " << status;
// Part 3: Finalization
// |DestroyEnclave| before exiting program.
asylo::EnclaveFinal empty_final_input;
status = manager->DestroyEnclave(client, empty_final_input);
LOG_IF(QFATAL, !status.ok()) << "DestroyEnclave failed with: " << status;
return 0;
}
The three enclave entry points are shown in the above code. Let’s go through
each part of the main() procedure.
Part 1: Initialization
The untrusted application performs the following steps to initialize the trusted application:
- Configures an instance of
EnclaveManagerwith default options. TheEnclaveManagerhandles all enclave resources in an untrusted application. - Configures a
EnclaveLoadConfigobject to specify options for the SgxLoadConfig to fetch the enclave binary image from disk. - Calls
EnclaveManager::LoadEnclaveto bind the enclave to the name"demo enclave". This call implicitly invokes the enclave’sInitializemethod.
Part 2: Secure execution
The untrusted application performs the following steps to securely execute a workload in the trusted application:
- Provides arbitrary input data in an
EnclaveInput. This example uses a single string protobuf extension to theEnclaveInputmessage. This extension field is used to pass data to the enclave for encryption. - Gets a handle to the enclave via
EnclaveManager::GetClient. - Invokes the enclave by calling
EnclaveClient::EnterAndRun. This method is the primary entry point used to dispatch messages to the enclave. It can be called an arbitrary number of times. - Receives the result from the enclave in an
EnclaveOutput. Developers can add protobuf extensions to theEnclaveOutputmessage to provide arbitrary output values from their enclave.
Part 3: Finalization
The untrusted application performs the following steps to finalize the trusted application:
- Provide arbitrary finalization data to the enclave and destroy the enclave
via
EnclaveManager::DestroyEnclave. - The Asylo framework will implicitly use the client to call the trusted
application’s
Finalizemethod.
Writing an enclave application
We just saw how to initialize, run, and finalize an enclave using the Asylo SDK.
These calls happen on the untrusted side of the enclave boundary. Now, let’s
take a look at the code on the trusted side. Building an enclave consists of
deriving from the TrustedApplication class and overriding a number of virtual
methods. Each method defines the logic to be invoked for an
enclave life cycle event.
class EnclaveDemo : public TrustedApplication {
public:
EnclaveDemo() = default;
Status Run(const EnclaveInput &input, EnclaveOutput *output) {
std::string user_message = GetEnclaveUserMessage(input);
std::string encrypt_message = EncryptMessage(user_message);
std::cout << "Encrypted message:" << std::endl
<< encrypt_message << std::endl;
return absl::OkStatus();
}
const std::string GetEnclaveUserMessage(const EnclaveInput &input) {
return input.GetExtension(enclave_input_test_string).test_string();
}
The class EnclaveDemo overrides its parent’s TrustedApplication::Run method
with its secure execution logic to encrypt a user message. This enclave does not
have any custom initialization or finalization logic, so neither of those
methods are overridden.
Enclave life cycle
The TrustedApplication class implements a model enclave which users may
customize with their application logic. Method input and output parameters are
protobufs defined by the Asylo SDK and are extensible with additional
user-defined content.
Initialization
The enclave may provide a handler that runs synchronously at the time the
enclave is loaded by EnclaveManager.
virtual Status TrustedApplication::Initialize(const EnclaveConfig &config);
The Asylo framework guarantees this entry point is invoked exactly once, and that no other thread may enter until this method completes successfully. If initialization fails and returns a non-OK status, no further entry into the enclave is possible.
Execution
After initialization has succeeded, threads may enter the enclave and run the
following handler via the client method EnclaveClient::EnterAndRun:
virtual Status TrustedApplication::Run(const EnclaveInput &input,
EnclaveOutput *output);
Many threads may invoke this entry point in parallel, so its implementation of
Run must be thread safe. The application author is responsible for ensuring
that concurrent access to data is managed appropriately.
Finalization
The last category of enclave entry is finalization.
virtual Status TrustedApplication::Finalize(const EnclaveFinal &final);
The Asylo runtime will make a best-effort attempt to invoke the enclave finalization entry point when either of the following occurs:
-
Untrusted code destroys the enclave by calling
EnclaveManager::DestroyEnclave. -
The host application exits and the
EnclaveManageritself is finalized.
The Asylo runtime guarantees that no further entry into the enclave is possible after finalization.
Note that in the case the enclave exits abnormally, or in the event the
untrusted runtime is compromised, it is not possible to guarantee that
Finalize is invoked. Applications should not rely on Finalize for
correctness or for security.